Introduction of Heritability
What is Heritability
The heritability of a trait within a population is the proportion of observable differences in a trait between individuals within a population that is due to genetic differences.
- Possible contributors to the variation between individuals in phenotypes can be a lot: genetics, environment, random chances, genetic and environment interaction, etc.
- Heritability analyzes the relative contributions of difference in genetic and non-genetic factors to the total phenotypic variance in a population.
- It is an important concept in quantitative genetics, particularly in selective breeding and behaviour genetics.
Statistical Definition
Any particular phenotype can be modelled as the sum of genetic and environmental effects:
- Phenotype (P) = Genotype (G) + Environment (E).
Thus the variance of the trait can be expressed as:
- Var(P) = Var(G) + Var(E) + 2 Cov(G,E).
There are two notes about this definition:
- In a planned experiment, Cov(G,E) can be controlled and held at 0.
- Genetic contribution, Var(G), includes additive, dominant, and epistatic(multi-genic interactions), as well as maternal, and paternal effects, where individuals are directly affected by their parents' phenotype . Because genetic contribution has a lot of variaties, we have two types of heritability definition relating to different types of genetic contribution.
Broad and Narrow Heritability
-
Broad sense Heritability is defined as:
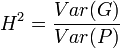
Note that here Var(G) contains all the genetic contributions to a population's phnotypic variance including additive, dominance, epistatic, maternal and paternal effects.
Narrow sense Heritability is defined as:
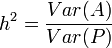
Note that here Var(A) only depicts the portion of variance that is due to additive(allelic) genetic effects.
Narrow sense heribatiliby is important for selection and breeding, because additive variance has close relationship with how much one trait mean in the next generation changes as a function of the trait mean of their parents. This leads to an estimation of the narrow sense heritability, see the example below:
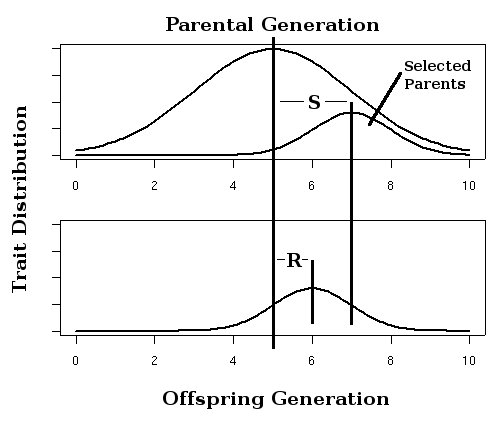
S: strengh of selection. R: response of selection. We have h2=R/S.
Several Notes on Heritability
-
Heritability is always relative to the genetic and environmental factors in the population. Heritability could increase if genetic variation increases, cuasing individuals to show more phnotypic variation. On the other hand, heritability might also increase if the environmental variation decreases, causing individuals to show less phenotypic variation. Hense, heritability is specific to a particular population in a particular environment.
A prerequisite for heritability analyses is that there is some population variation to account for.e.g, If we want to study heritability of hair color, and the hair color of the target population is all totally black, then the heritability cannot be estimated